

NanoAndMore proudly sponsors the #AVS67 Virtual Showcase this weekTue Oct 27 2020
NanoAndMore proudly sponsors the #AVS67 Virtual Showcase this week. It is being held October 27-29 10:00 am-1:15 pm. (EDT) and covers a range of emerging topics related to #materialsprocessing and interfaces in the research and manufacturing communities. Live sessions ( the first one starts at 10 a.m. EDT today ) are available and participation is free of charge. Haven’t registered yet? Have a look at: https://avs67.avs.org


Molecular and nanoscale evaluation of N-cadherin expression in invasive bladder cancer cells under control conditions or GW501516 exposureMon Oct 26 2020
In the article “Molecular and nanoscale evaluation of N-cadherin expression in invasive bladder cancer cells under control conditions or GW501516 exposure” Céline Elie-Caille, Isabelle Lascombe, Adeline Péchery, Hugues Bittard and Sylvie Fauconnet, describe how they aimed at exploring the expression level of N-cadherin in invasive bladder cancer cells upon GW501516 exposure by both molecular biology techniques such as RTqPCR and Western blotting and Atomic Force Microscopy ( AFM ) using NanoWorld Pyrex-Nitride silicon nitride PNP-TR AFM tips functionalized with a monoclonal antibody directed against this adhesion molecule. *
Please have a look at the NanoWorld® blog for the full citation and a direct link to the full article.


Yeast Nanometric Scale Oscillations Highlights Fibronectin Induced Changes in C. AlbicansMon Oct 19 2020
Yeast resistance to antifungal drugs is a major public health issue. Fungal adhesion onto the host mucosal surface is still a partially unknown phenomenon that is modulated by several actors among which fibronectin plays an important role. Targeting the yeast adhesion onto the mucosal surface could lead to potentially highly efficient treatments. *
In the article “Yeast Nanometric Scale Oscillations Highlights Fibronectin Induced Changes in C. Albicans” Anne-Céline Kohler, Leonardo Venturelli, Abhilash Kannan, Dominique Sanglard, Giovanni Dietler, Ronnie Willaert and Sandor Kasas, explore the effect of fibronectin on the nanomotion pattern of different Candida albicans strains by atomic force microscopy ( AFM )-based nanomotion detection and correlated the cellular oscillations to the yeast adhesion onto epithelial cells. *
Please have a look at the NANOSENSORS blog for the full citation and a direct link to the full article.


Electrochromic switching of tungsten oxide films grown by reactive ion-beam sputter depositionTue Oct 13 2020
The building sector and within it the class of so-called smart windows plays an important role in terms of energy saving potential. Chromogenic thin films are crucial building blocks in smart windows to modulate the flux of visible light and heat radiation into buildings.
In “Electrochromic switching of tungsten oxide films grown by reactive ion-beam sputter deposition” Mario Gies et al. describe how Tungsten oxide thin films were grown by ion-beam sputter deposition (IBSD) and then show the possibility of influencing samples characteristics by using different preparation parameters. This allows to tune the elemental composition, optical properties or to influence the structure and the degree of crystallization in the resulting thin films.
NanoWorld® Pointprobe® SEIHR AFM probes designed for soft non-contact mode imaging were used for the AFM investigations described in the cited article. https://www.nanoworld.com/pointprobe-seiko-instruments…
Please have a look at the NanoWorld blog for the full citation and a link to the full article
https://www.nanoworld.com/blog/electrochromic-switching-of-tungsten-oxide-films-grown-by-reactive-ion-beam-sputter-deposition/
https://www.nanoworld.com/blog/electrochromic-switching-of-tungsten-oxide-films-grown-by-reactive-ion-beam-sputter-deposition/

How does this technique work with Atomic Force Microscopy and ångström?Thu Oct 08 2020
How does this technique work with Atomic Force Microscopy and ångström?


BudgetSensors® diamond-coated All-In-One-DD AFM probes used in a recent studyTue Oct 06 2020
Extracting indentation modulus at the nanoscale via white-noise excitation in Stochastic Atomic Force Acoustic Microscopy (S-AFAM) with the help of BudgetSensors® diamond-coated All-In-One-DD AFM probes.


Multi-Channel Exploration of O Adatom on TiO2(110) Surface by Scanning Probe MicroscopyTue Oct 06 2020
In the article “Multi-Channel Exploration of O Adatom on TiO2(110) Surface by Scanning Probe Microscopy” Huan Fei Wen, Yasuhiro Sugawara and Yan Jun describe how they studied the O2 dissociated state under the different O2 exposed temperatures with atomic resolution by scanning probe microscopy (SPM) and imaged the O adatom by simultaneous atomic force microscopy (AFM)/scanning tunneling microscopy (STM).*
The effect of AFM operation mode on O adatom contrast was investigated, and the interaction of O adatom and the subsurface defect was observed by AFM/STM. Multi-channel exploration was performed to investigate the charge transfer between the adsorbed O and the TiO2(110) by obtaining the frequency shift, tunneling current and local contact potential difference at an atomic scale. The tunneling current image showed the difference of the tunneling possibility on the single O adatom and paired O adatoms, and the local contact potential difference distribution of the O-TiO2(110) surface institutively revealed the charge transfer from TiO2(110) surface to O adatom. The experimental results are expected to be helpful in investigating surface/interface properties by SPM. *
Iridium-coated ultrastiff AFM cantilever SD-T10L100 from the NANOSENSORS Special Developments List (typical Force constant 2 000 N/m) were used in the presented study.
The cantilever tip was first degassed at approximately 650 K for 30 min and then cleaned by Ar ion bombardment to remove the contaminants, prior to the measurements. Features of the surface structure were related to the charge states of the tip apex, and a stable tip was essential to accurately characterize the surface structure and properties in the experiment. The imaging mode became stable in AFM experiments when the metal-coated Si cantilever was employed in the experiments. *
Please have a look at the NANOSENSORS blog for the full citation and a direct link to the full article.


MikroMasch® HQ:CSC17/No Al used in a recent studyThu Oct 01 2020
AFM-based nanomechanical study of ovarian tissues with pathological conditions using MikroMasch® HQ:CSC17/No Al AFM probes.

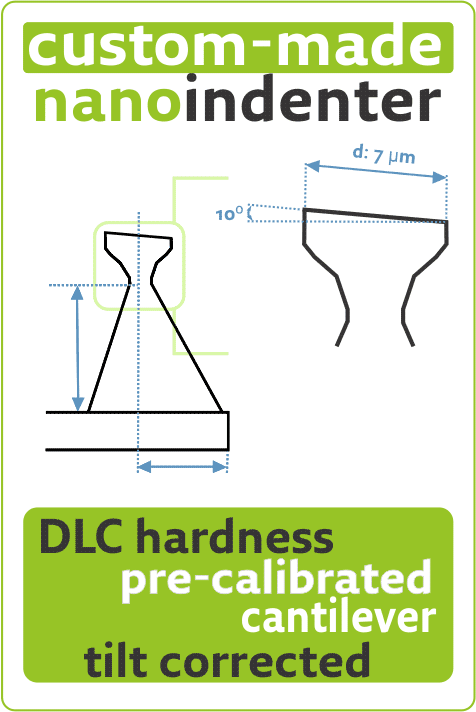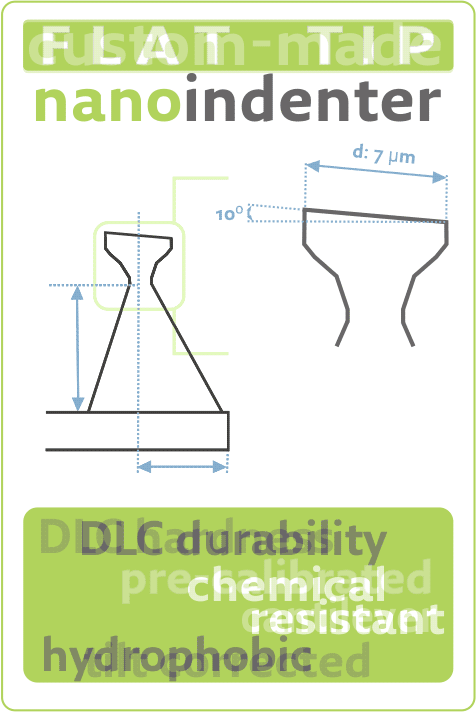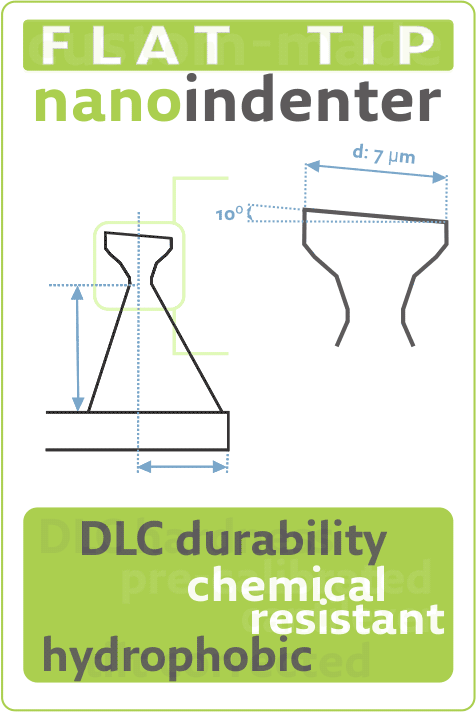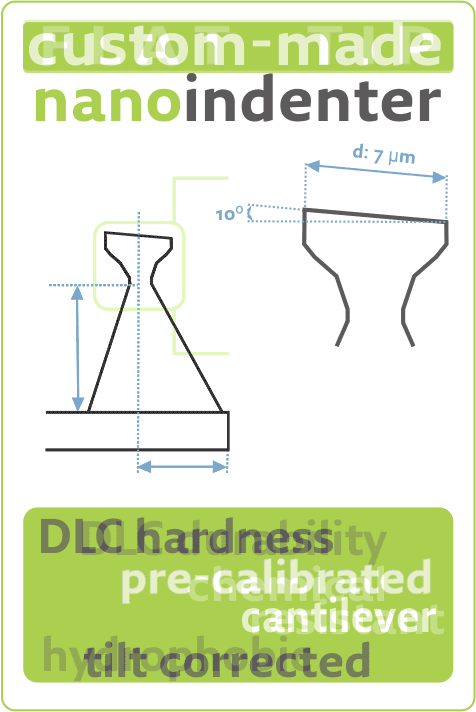
Nanotools tilt-corrected M-CIS applied to measure Patterned Sapphire SubstrateThu Oct 01 2020
Discover how very durable nanotools tilt-corrected M-CIS #AFMprobes with 400 nm length and 4˚ half cone angle https://www.nanotools.com/…/high-aspect-ratio/m-cis.html are applied to measure height, diameters, pitch, and side angles of Patterned #SapphireSubstrate ( PSS ) in the latest nanotools blogpost. https://www.nanotools.com/blog/index.html


Influence of orientation and ferroelectric domains on the photochemical reactivity of La2Ti2O7Mon Sep 28 2020
In the article “Influence of orientation and ferroelectric domains on the photochemical reactivity of La2Ti2O7” Mingyi Zhang, Paul A. Salvador and Gregory S. Rohrer describe how they measured the effects of crystal orientation and ferroelectric domain structure on the photochemical reactivity of La2Ti2O7. *
The reactivity is greatest on (001) surfaces (this is the orientation of the layers in this (110)p layered perovskite structure) while surfaces perpendicular to this orientation have the least reactivity. Complex domain structures were observed within the grains, but they appeared to have no effect on the photocathodic reduction of silver, in contrast to previous observations on other ferroelectrics. La2Ti2O7 is an example of a ferroelectric oxide in which the crystal orientation has a greater influence on the photochemical reactivity than polarization from the internal domain structure. *
NanoWorld™ conductive Platinum Iridium coated Arrow-EFM AFM probes were used for the Piezo-force microscopy (PFM) that was used to determine the ferroelectric domain structure on the surface. * https://www.nanoworld.com/electrostatic-force-microscopy…
The ferroelectric domains on the surface were found to have irregular shapes and there was no correlation between the pattern of silver reduction and the domain shape. The results indicate that the ferroelectric polarization of La2Ti2O7 does not alter the reactivity enough to overcome the influence of the anisotropic crystal structure. *
Please have a look at the NanoWorld blogpost for the full citation and a direct link to the full article.


Macroscopic manifestation of domain-wall magnetism and magnetoelectric effect in a Néel-type skyrmion hostTue Sep 22 2020
In the article “Macroscopic manifestation of domain-wall magnetism and magnetoelectric effect in a Néel-type skyrmion host” Korbinian Geirhos, Boris Gross, Bertalan G. Szigeti, Andrea Mehlin, Simon Philipp, Jonathan S. White, Robert Cubitt, Sebastian Widmann, Somnath Ghara, Peter Lunkenheimer, Vladimir Tsurkan, Erik Neuber, Dmytro Ivaneyko, Peter Milde, Lukas M. Eng, Andrey O. Leonov, Sándor Bordács, Martino Poggio and István Kézsmárki report a magnetic state in GaV4Se8 which emerges exclusively in samples with mesoscale polar domains and not in polar mono-domain crystals.*
It is manifested by a sharp anomaly in the magnetic susceptibility and the magnetic torque, distinct from other anomalies observed also in polar mono-domain samples upon transitions between the cycloidal, the Néel-type skyrmion lattice and the ferromagnetic states. *
The authors ascribe this additional transition to the transformation of distinct magnetic textures, confined to polar domain walls (DW), to the ferromagnetic (FM) state. The emergence of these DW-confined magnetic states is likely driven by the mismatch of different spin spirals, hosted by the adjacent domains. A clear anomaly in the magneto-current indicates that the DW-confined magnetic states also have strong contributions to the magnetoelectric response. *
The authors expect polar DWs to commonly host such confined magnetic edge states and, thus, offer a fertile ground to explore novel forms of magnetism. *
To characterize the polar domains and to estimate the density of DWs in GaV4Se8, K. Geirhos et al. combined several complementary scanning probe microscopy techniques, including non-contact atomic force microscopy ( nc-AFM ), scanning dissipation microscopy ( SDM ), and frequency-modulated Kelvin-probe force microscopy ( KPFM ). *
In attempt to observe spin cycloidal and Néel-type skyrmion textures within polar domains of GaV4Se8, only evidenced by small-angle neutron scattering measurements so far43, the authors of the article also carried out magnetic force microscopy (MFM) measurements. A second purpose of the MFM study was to explore possible magnetic states confined to the vicinity of DWs, as reported in GaV4S8. *
NANOSENSORS™ SSS-QMFMR high resolution magnetic AFM probes for ultra high vacuum conditions were used for the magnetic measurements with scanning probe microscopy. * https://www.nanosensors.com/supersharpsilicon-high-quality…
NANOSENSORS™ conductive wear-resistant Platinum Silicide AFM probes of the PtSi-FM type were used for all other measurements described in the article. * https://www.nanosensors.com/platinum-silicide-force…
Please have a look at the NANOSENSORS blog for the full citation and a direct link to the full article.


Carbon nanotube porin diffusion in mixed composition supported lipid bilayersTue Sep 15 2020
Lipid membranes play a key role in living systems by providing a structural barrier that separates cellular compartments. Bilayer fluidity in the lateral plane is a key property of lipid membranes, that allows the membrane to have sufficient flexibility to accommodate dynamic stresses, shape changes and rearrangements accompanying the cellular lifecycle.*
In the article “Carbon nanotube porin diffusion in mixed composition supported lipid bilayers” Kylee Sullivan, Yuliang Zhang, Joseph Lopez, Mary Lowe and Aleksandr Noy describe how they used high-speed atomic force microscopy (HS-AFM) and all-atom molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to study the behavior of CNTPs in a mixed lipid membrane consisting of DOPC lipid with a variable percentage of DMPC lipid added to it. HS-AFM data reveal that the CNTPs undergo diffusive motion in the bilayer plane.*
Motion trajectories extracted from the HS-AFM movies indicate that CNTPs exhibit diffusion coefficient values broadly similar to values reported for membrane proteins in supported lipid bilayers. The data also indicate that increasing the percentage of DMPC leads to a marked slowing of CNTP diffusion. MD simulations reveal a CNTP-lipid assembly that diffuses in the membrane and show trends that are consistent with the experimental observations. *
The above-mentioned study confirms that CNTPs mimic the major features of the diffusive movement of biological pores in lipid membranes and shows how the increase in bilayer viscosity leads to a corresponding slowdown in protein motion. It should be possible to extend this approach to studies of other membrane protein dynamics in supported lipid bilayers. The authors note that those studies, however, will need to be mindful of the challenge of unambiguous visualization of the membrane components, especially in systems that incorporate smaller proteins, such as antimicrobial peptides. Another challenge that could complicate these studies would be microscopic phase separation of the lipid matrix that could lead to complicated pore dynamics in the membrane. *
NanoWorld Ultra-Short AFM cantilevers with high-density carbon/diamond-like carbon (HDC/DLC) AFM tips of the USC-F1.2-k0.15 type were used for the high-speed atomic force microscopy described in the article. * https://www.nanoworld.com/Ultra-Short-Cantilevers-USC-F1.2…
Please have a look at the NanoWorld blog for the full citation and a direct link to the full article.


Check out the BudgetSensors® Combo BoxThu Sep 10 2020
BudgetSensors’ unique BudgetComboBox allows you to compile your personalized box of different AFM probes.
With the BudgetComboBox you take advantage of our built-in volume discounts for boxes of 50 probes without having to order 50 identical AFM probes.


Plant-Based Scaffolds Modify Cellular Response to Drug and Radiation Exposure Compared to Standard Cell Culture ModelsTue Sep 08 2020
Plant-based scaffolds present many advantages over a variety of biomaterials.*
Recent studies explored their potential to be repopulated with human cells and thus highlight a growing interest for their use in tissue engineering or for biomedical applications. However, it is still unclear if these in vitro plant-based scaffolds can modify cell phenotype or affect cellular response to external stimuli.*
In the research article “Plant-Based Scaffolds Modify Cellular Response to Drug and Radiation Exposure Compared to Standard Cell Culture Models “ Jerome Lacombe, Ashlee F. Harris, Ryan Zenhausern, Sophia Karsunsky and Frederic Zenhausern report the characterization of the mechano-regulation of melanoma SK-MEL-28 and prostate PC3 cells seeded on decellularized spinach leaves scaffolds, compared to cells deposited on standard rigid cell culture substrate, as well as their response to drug and radiation treatment.*
In their study the authors show that plant decellularization provide soft scaffolds that match the stiffness range of most of the human tissue and modify cell behavior, including drug and radiation response, compared to standard cell culture models. Because of their distinguished features (natural vasculature, low immunogenicity, low cost, relative ease, etc.) and their wide variations in the shape and structures, these scaffolds offer a multi-controllable model with multiple biochemical and biophysical interactions. However, additional studies are required to determine if they could address important architectural and physical challenges of the in vivo tissue environment.
For force measurement, the Young’s Modulus (YM) of the leaf scaffolds were determined using force spectroscopy mode at liquid interface with NANOSENSORS uniqprobe qp-BioAC AFM probes for leaves measurement.* https://www.nanosensors.com/uniqprobe-uniform-quality…
Please have a look at the NANOSENSORS blog for the full citation and a direct link to the full research article.


Photoresponsive Photoacid-Macroion Nano-AssembliesMon Aug 31 2020
In mother nature, the concept of self-assembly is vital for life, as it generates much of the functionality of living cells. It also bears great synthetic potential for the formation of versatile, switchable, and functional nanostructures.*
Noncovalent interactions can be triggered by external influences, such as the change of pH, light irradiation, thermal activation, introduction of a magnetic field, moisture, or redox response. Of high interest are light-responsive systems, for example in the fields of sensors or therapy, and, thus, it is desirable to explore novel concepts toward light-triggerable self-assembly.*
In the article “Photoresponsive Photoacid-Macroion Nano-Assemblies” Alexander Zika, Sarah Bernhardt and Franziska Gröhn present light-responsive nano-assemblies with light-switchable size based on photoacids.*
Anionic disulfonated napthol derivates and cationic dendrimer macroions are used as building blocks for electrostatic self-assembly. Nanoparticles are already formed under the exclusion of light as a result of electrostatic interactions. Upon photoexcitation, an excited-state dissociation of the photoacidic hydroxyl group takes place, which leads to a more highly charged linker molecule and, subsequently, to a change in size and structure of the nano-assemblies. The effects of the charge ratio and the concentration on the stability have been examined with absorption spectroscopy and -potential measurements.*
The influence of the chemical structure of three isomeric photoacids on the size and shape of the nanoscale aggregates has been studied by dynamic light scattering and atomic force microscopy, revealing a direct correlation of the strength of the photoacid with the changes of the assemblies upon irradiation.*
NanoWorld Ultra-Short AFM Cantilevers of the USC-F0.3-k0.3 type ( typical force constant 0.3 N/m ) were operated in tapping mode for the Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) images presented in the article.* https://www.nanoworld.com/Ultra-Short-Cantilevers-USC-F0.3…
Please have a look at the NanoWorld blog for the full citation and a direct link to the full article.


Large-Area Graphene Oxide Films for Supercapacitor Electrodes, Transparent Conductive Films and FET'sWed Aug 26 2020
Nanotools tilt-corrected EBD-HAR high aspect ratio #AFMprobes https://www.nanoandmore.com/AFM-Probe-EBD-HAR with 800 nm length and 4˚ half cone angle featured in the interesting research article "Sensor characterization by comparative measurements using a multi-sensor measuring system" by Sebastian Hagemeier et al. Find out more in the nanotools blog https://www.nanotools.com/blog/index.html


Electric-field-driven non-volatile multi-state switching of individual skyrmions in a multiferroic heterostructureMon Aug 24 2020
Electrical manipulation of skyrmions attracts considerable attention for its rich physics and promising applications. To date, such a manipulation is realized mainly via spin-polarized current based on spin-transfer torque or spin–orbital torque effect.*
However, this scheme is energy consuming and may produce massive Joule heating. To reduce energy dissipation and risk of heightened temperatures of skyrmion-based devices, an effective solution is to use electric field instead of current as stimulus.*
In the article “Electric-field-driven non-volatile multi-state switching of individual skyrmions in a multiferroic heterostructure”, Yadong Wang, Lei Wang, Jing Xia, Zhengxun Lai, Guo Tian, Xichao Zhang, Zhipeng Hou, Xingsen Gao, Wenbo Mi, Chun Feng, Min Zeng, Guofu Zhou, Guanghua Yu, Guangheng Wu, Yan Zhou, Wenhong Wang, Xi-xiang Zhang and Junming Liu realize an electric-field manipulation of skyrmions in a nanostructured ferromagnetic/ferroelectrical heterostructure at room temperature via an inverse magneto-mechanical effect.*
Intriguingly, such a manipulation is non-volatile and exhibits a multistate feature. Numerical simulations indicate that the electric-field manipulation of skyrmions originates from strain-mediated modification of effective magnetic anisotropy and Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction.*
The results presented in the article open a direction for constructing low-energy-dissipation, non-volatile, and multistate skyrmion-based spintronic devices.*
To minimize the influence of the magnetic field from the MFM tip on the magnetic domain structure during the magnetic force microscopy ( MFM ) measurements, NANOSENSORS™ PPP-LM-MFMR low moment magnetic AFM probes were used.* https://www.nanosensors.com/pointprobe-plus-magnetic-force…
These MFM probes are designed for magnetic force microscopy with reduced disturbance of the magnetic sample by the tip and enhanced lateral resolution compared to the standard PPP-MFMR probe. The distance between the tip and sample was maintained at a constant distance of 30 nm.*
Please have a look at the NANOSENSORS blog for the full citation and a direct link to the full article.


Single molecule secondary structure determination of proteins through infrared absorption nanospectroscopyMon Aug 24 2020
Determining secondary structure of single protein molecules with off-resonance short pulse infrared nanospectroscopy using MikroMasch HQ:NSC36/Al BS AFM probes.

NanoWorld Screencast on Ultra-Short Cantilevers (USC) for High-Speed AFM (HS-AFM) and video rate Atomic Force Microscopy passes 1000 views markMon Aug 17 2020
The NanoWorld screencast on Ultra-Short Cantilevers (USC) for High Speed AFM (HS-AFM) and video rate Atomic Force Microscopy held by Mathieu Burri has just reached the 1000 views mark. Congratulations Mathieu!
The Ultra-Short Cantilevers series https://www.nanoworld.com/ultra-short-cantilevers-afm-tips combines very small cantilevers capable of resonating in the MHz regime and a very sharp and wear resistant tip and is dedicated to High-Speed AFM (HS-AFM). The Ultra-Short Cantilevers series consists of six different types of probes which cover the complete range of high speed scanning applications, from non-contact mode to contact mode, from measurements in air to measurements in liquid.
More information such as high speed videos, an image gallery and a regularly updated reference list of scientific articles on high speed AFM can be found on the dedicated website: https://www.highspeedscanning.com/ . You can also find references to scientific articles mentioning the use of NanoWorld USC AFM probes on the NanoWorld blog.
If you haven’t seen the USC screencast yet have a look.

Tailoring a magnetization process with BudgetSensors MagneticMulti75-G MFM AFM probesThu Aug 13 2020
Tailoring the magnetization process of the magnetic materials studied with BudgetSensors MagneticMulti75-G MFM AFM probes.

















