

MCNT-300™: 18 nm cylindrical tip for durable and consistent bottom access of finest featuresTue Nov 16 2021
Blue Line product highlight:
MCNT-300™: Amorphous CNT solution for demanding depth metrology applications
- Controlled shape:
Precisely controlled length of 300 nm and uniform width of 18 nm - Controlled orientation: 3° or 12°
Tilt compensation within ±0.5° for enhanced access capabilities to bottom trench features - Optimized cantilevers:
Standard with k: 40 N/m, f: 320 KHz
Softer cantilevers for force-controlling scanning modes available upon request - Diamond-like hardness and durability:
Exceptional wear resistance of diamond-like carbon for consistent
performance and reduced cost per measurement - Delivered with TrueDimensions™:
Datasheet for every single probe available online 24/7 via QR code




Happy World Science Day for Peace and Development!Wed Nov 10 2021


Correlation of membrane protein conformational and functional dynamicsFri Nov 05 2021
Membrane proteins (MPs) reside in the plasma membrane and perform various biological processes including ion transport, substrate transport, and signal transduction.*
Function-related conformational changes in membrane proteins occur in times scales ranging from nanoseconds to seconds.*
Continue reading...


Supercritical carbon dioxide decellularization of plant material to generate 3D biocompatible scaffoldsFri Oct 29 2021
Biocompatible scaffolds that can be repopulated with human cells have many uses such serving as replacement organs and tissues. Therefore there is an increasing interest in plant-based biomaterials for tissue engineering.*
As the above mentioned scaffolds should mimic the in vivo tissue environment closely they need to provide a fitting structural and biomechanical support to the cells while at the same time promoting cell behaviour and tissue development. *
Read more...


German National Metrology Institute (PTB) Scientists Present Nanomechanical Head with Exchangeable AFM Probes As IndenterWed Oct 20 2021
- Title: A MEMS nanoindenter with an integrated AFM cantilever gripper for nanomechanical characterization of compliant materials
DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/ab88ed - Authors: Z Li, S Gao, U Brand, K Hiller and H Wolff
- Publication: Nanotechnology
- Publisher: IOP Publishing
- Date: 11 May 2020


MikroMasch® shared a video - how to fabricate a photo on a silicon wafer using nanotechnologySat Oct 09 2021


BudgetSensors® celebrates Niels Bohr birthdayThu Oct 07 2021

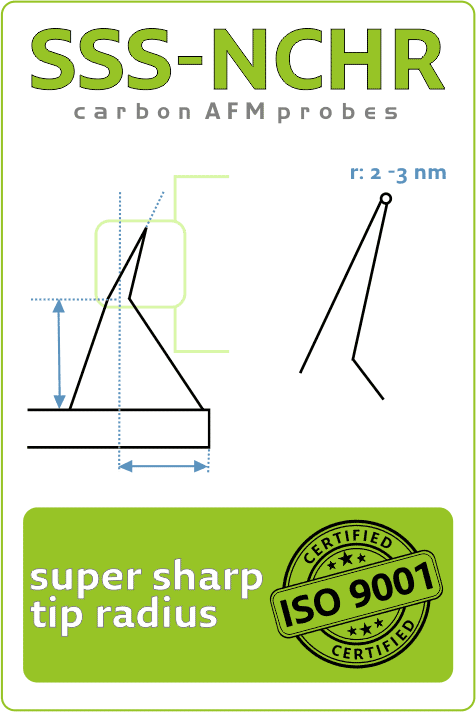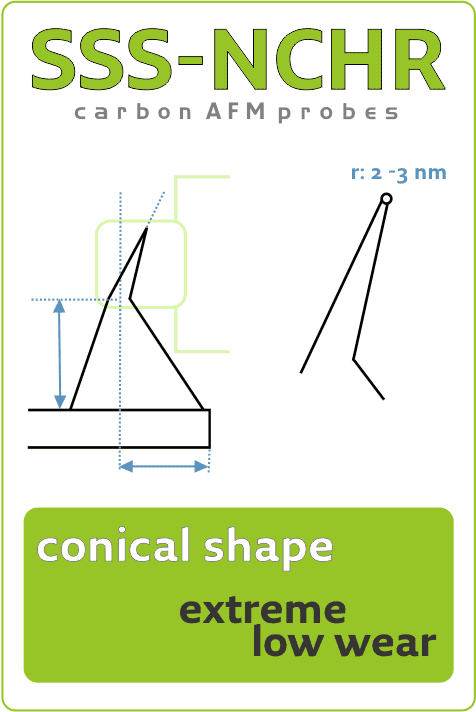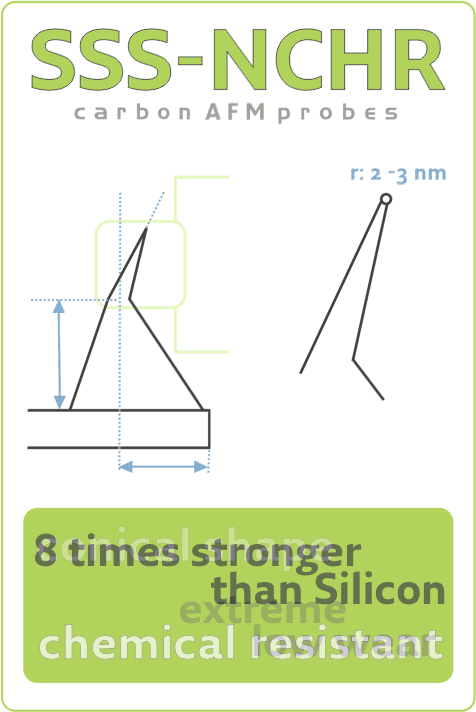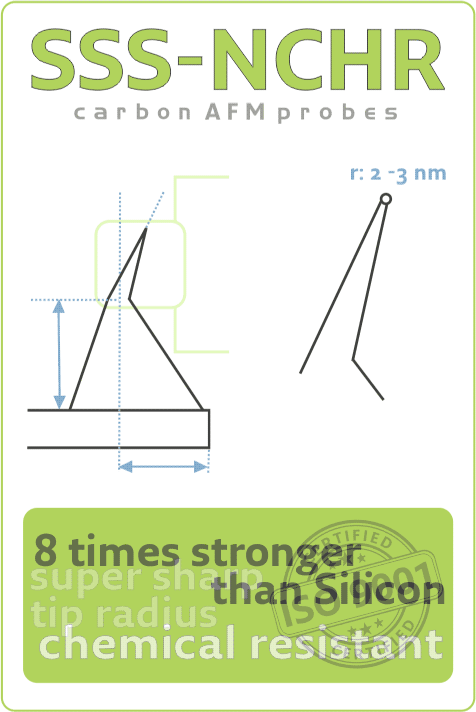
BOSCH and KIT Researchers Explore Tip Wear and Tip Shape Impact on Measurement Uncertainty During Thermal Grooving AFM StudyTue Sep 14 2021
- Title: A thermal grooving study of relative grain boundary energies of nickel in polycrystalline Ni and in a Ni/YSZ anode measured by atomic force microscopy
- Authors: Patricia Haremski, Lars Epple, Matthias Wieler, Piero Lupetin, Richard Thelen, Michael J. Hoffmann
- Publication: Acta Materialia
- Publisher: Elsevier
- Date: 1 August 2021
#AFM #metrology #topography #microscopy #nanotechnology #BOSCH #KIT


BudgetSensors® diamond-like carbon coated Tap300DLC AFM tips used in a recent studyThu Sep 09 2021


MikroMasch® thanks Ernest Rutherford for his experiment.Mon Aug 30 2021


Beetles Elytra, a model structure for next-generation bioinspired synthetic materialsFri Aug 13 2021
- Title: A matter of size? Material, structural and mechanical strategies for size adaptation in the elytra of Cetoniinae beetles
- Authors: Meisam Asgari, Nicolas A. Alderete, Zhaowen Lin, Ryan Benavides, Horacio D. Espinosa
- Publication: Acta Biomaterialia
- Publisher: Elsevier
- Date: 1 March 2021


HQ:XSC11/No Al used in a recent studyWed Jul 28 2021


Happy birthday to Gerd Binnig!Tue Jul 20 2021

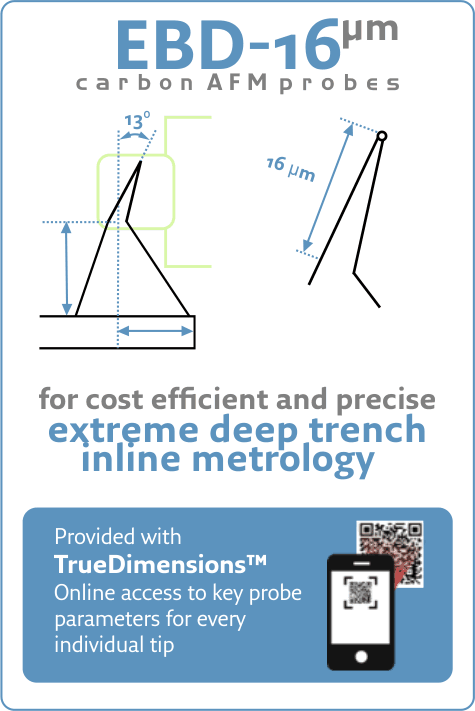
EBD-16: Semi Fab proven solution for extreme deep trench metrologyWed Jul 14 2021
Blue Line product highlight:
EBD-16™: World's longest high-performance AFM tip.
- Optimized conical shape for enhanced stability
Precisely controlled DLC spike length > 16 µm (Total tip length > 26 µm) - Controlled orientation: 12°, 13° or 3°
Tilt compensation for enhanced access to bottom trench features - Diamond-like hardness and durability
Unmatched wear resistance for consistent depth data, enhanced throughput, and reduced cost per measurement - Optimized cantilevers
Standard with k: 40 N/m, f: 320 kHz. Softer cantilevers available. - Delivered with TrueDimensions™
Datasheet for every single probe available online 24/7 via QR code


Images of collagen adsorbed to mica collected with HQ:NSC15/Al BS AFM probesTue Jun 29 2021


NANOSENSORS Membrane Surface Stress Sensors (MSS) used by NECThu Jun 24 2021


Tap300Al-G AFM probes used in a recent study.Thu Jun 17 2021


MikroMasch® celebrates Heinrich Rohrer's birthday!Thu Jun 10 2021

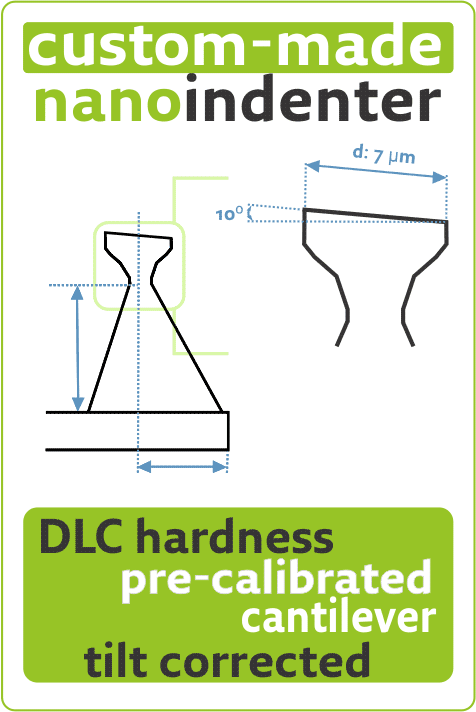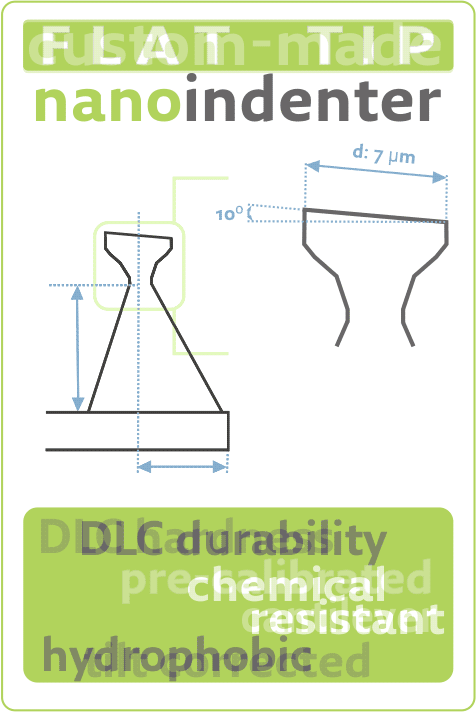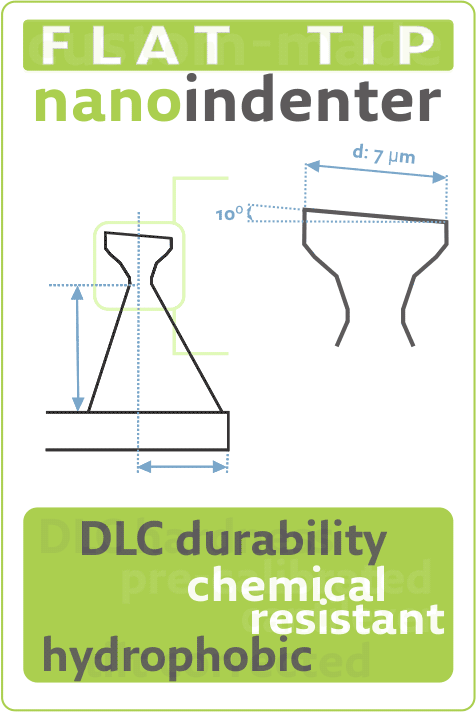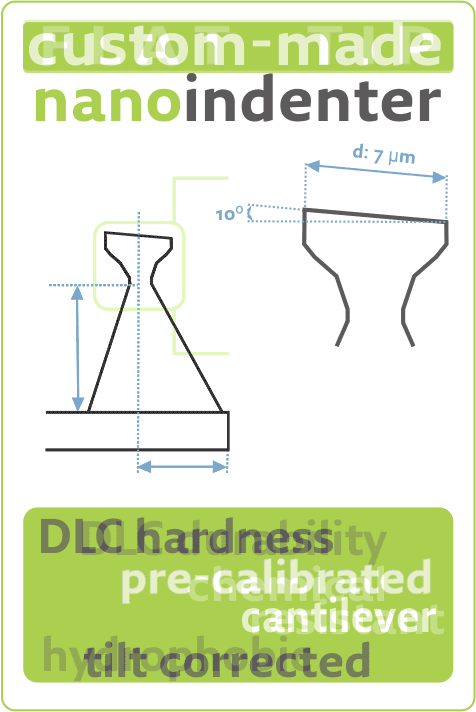
Flat Tip Effectively Avoids Tip-derived Youngs Modulus Errors Introduced by Conventional TipsMon May 31 2021
- Title: Evaluating Young's Modulus of Single Yeast Cells Based on Compression Using an Atomic Force Microscope with a Flat Tip
- Authors: Di Chang, Takahiro Hirate, Chihiro Uehara, Hisataka Maruyama, Nobuyuki Uozumi, Fumihito Arai
- Publication: Microscopy and Microanalysis
- Publisher: Cambridge University Press
- Date: Jan 15, 2021

















